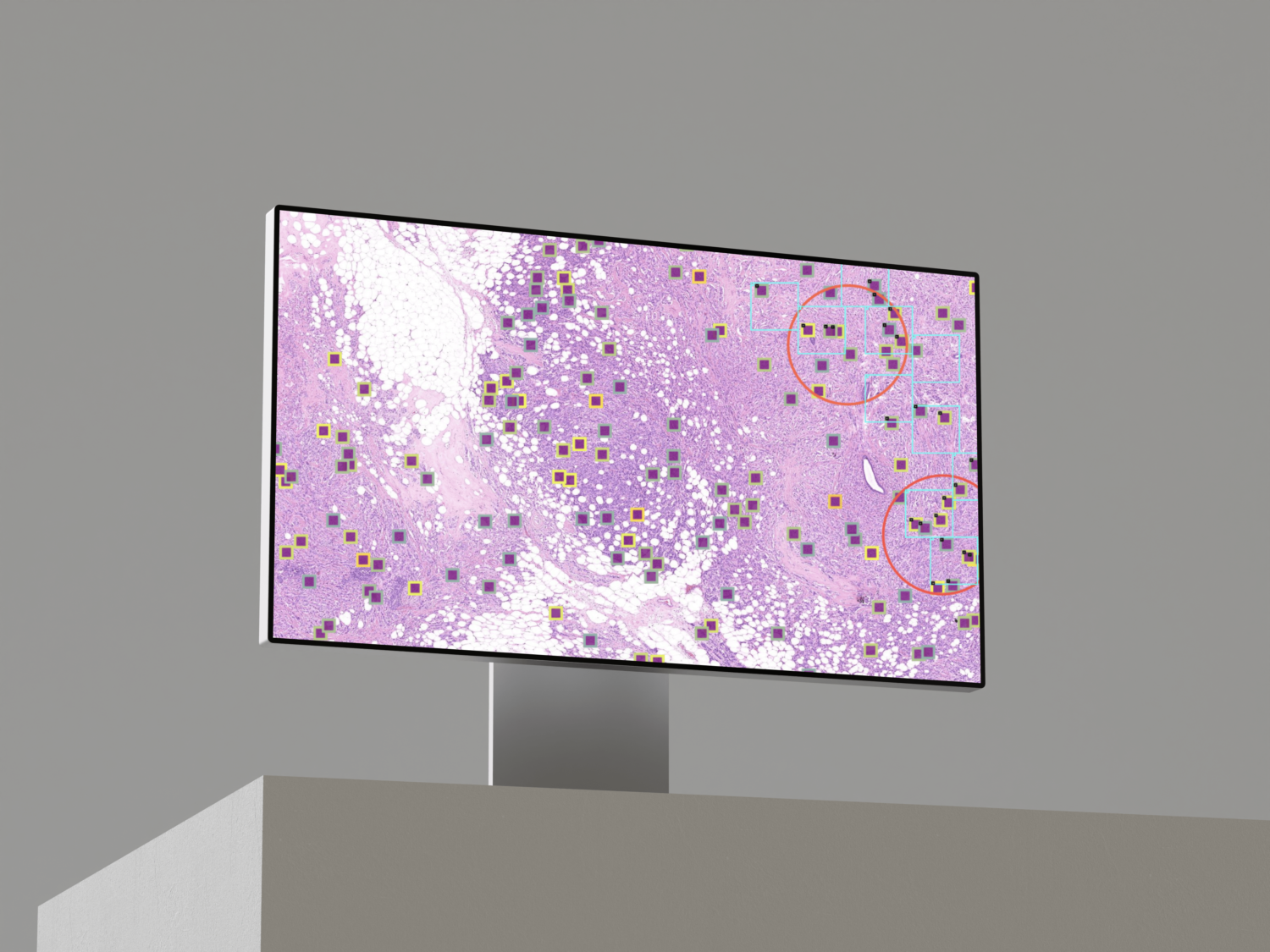
TILS - INVASIVE DUCTAL CARCINOMA
An automated TILs scoring Tool.
By : Rémy Peyret (Primaa), Stéphane Sockeel (Primaa), Anthony Moreau (Primaa), Marianne Petit (CHU de Lille), Samuel Touioui (CHU de Nancy), Elisabeth Lanteri (Medipath France), Bastien Jean Jacques (CHU de Caen), Marie Sockeel (Primaa), and Julien Adam (Hôpital Saint Joseph, Paris).
Introduction
TILs score has been identified by specialists to hold high predictive and prognostic value for Her2 positive and Triple Negative breast cancer [1]. While accurate protocols have been developed for its evaluation, pathologists demonstrate significant inter- and intra-observer variability attributed to cognitive biases [2]. The guidelines go as follows:
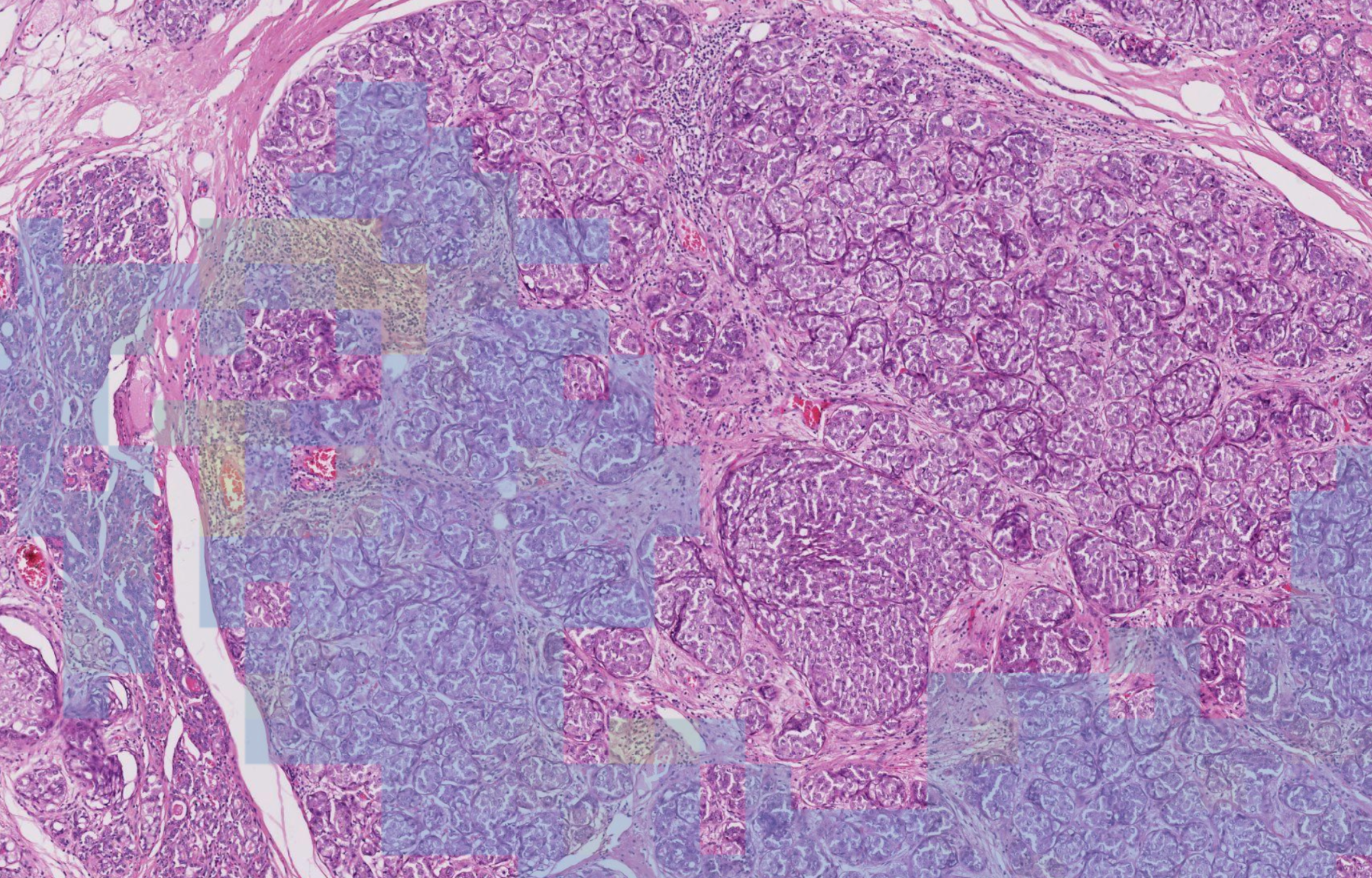
- Identify the Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) bench
- Identify tumour-associated stroma within it
- Calculate percentage of stroma occupied by TILs
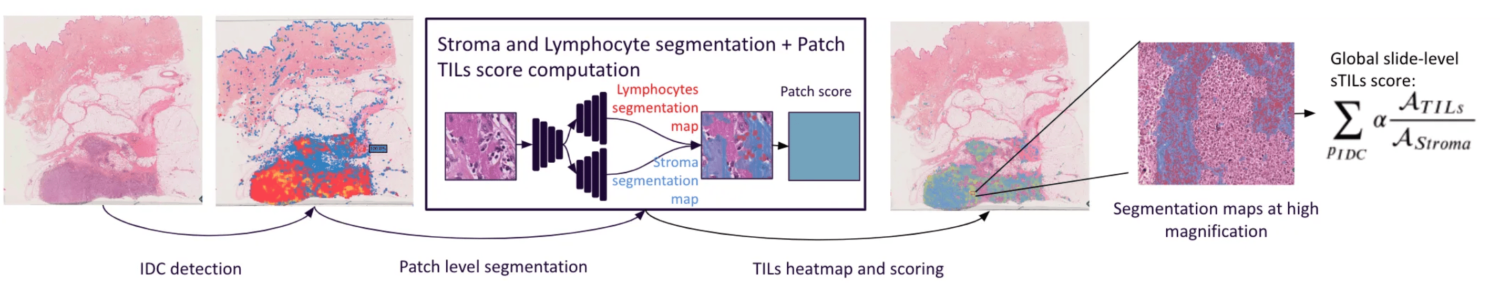
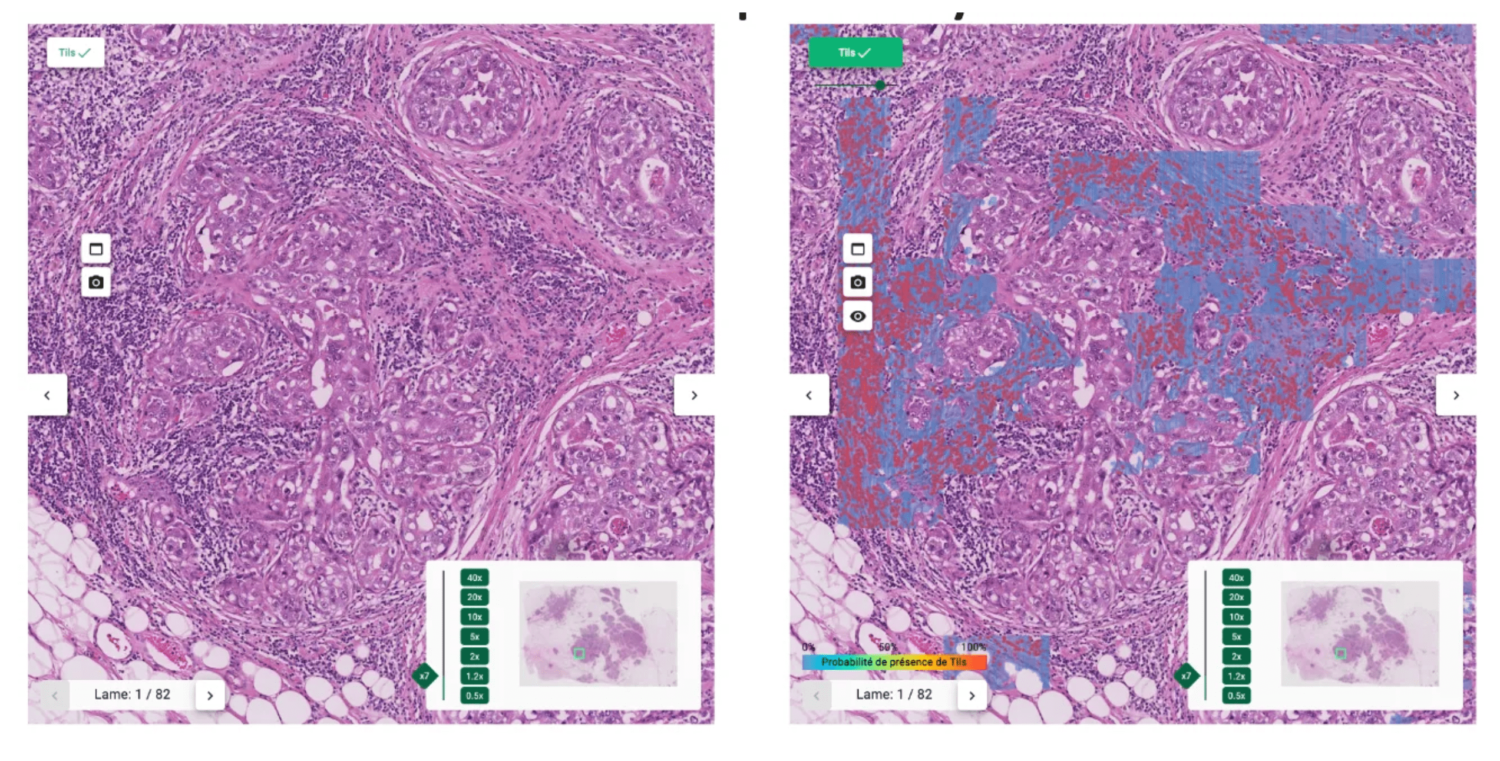
These guidelines served as basis for developing our automated TILs scoring tool as described on Fig. 1. A comprehensive interface (Fig. 2) was built to display results, providing explicability and mitigating cognitive biases.
Material and Method
- A patch-classification network with an EfficientNet B1 architecture was trained using cycleGAN stain augmentation for generalisation [4].
- A U-Net like deep learning network with a ResNet backbone followed by a double deconvolution head for stroma and lymphocytes semantic segmentations.
- The publicly available Tiger Dataset is used for this study. [3]
- WSIROIS (195 slides, 1879 ROIs): all ROIs along with their labels was used for training and testing the segmentation model.
- WSITILS (82 slides): slides were used for testing the final scores. For better reliability, the annotation was performed internally by 3 experienced pathologists. The average score is used as the ground truth.
Results and Discussion
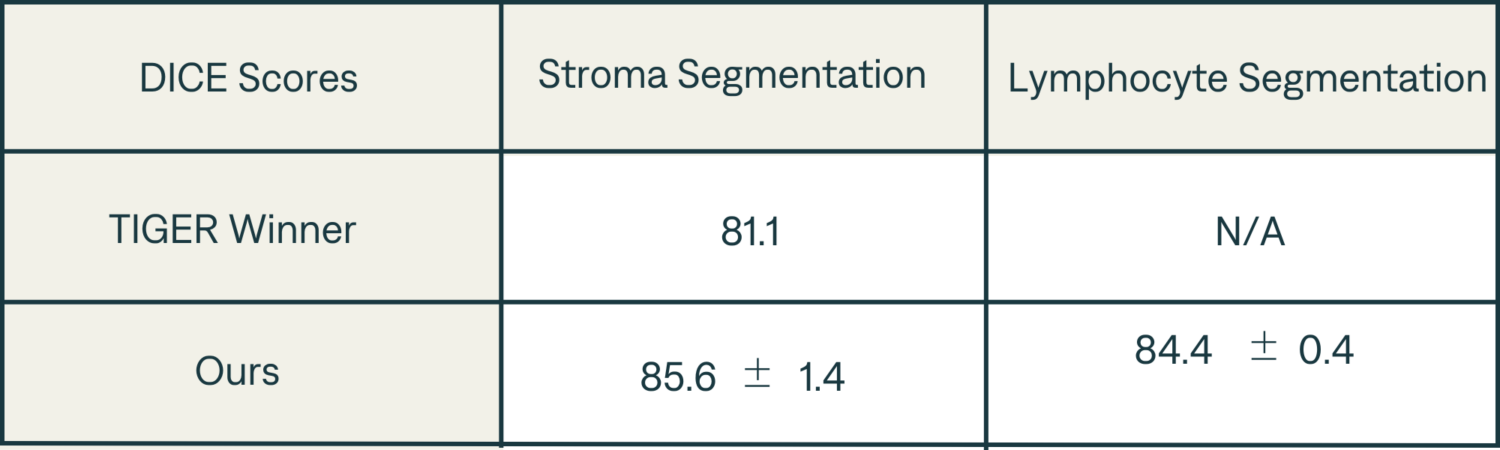
- Segmentation DICE scores are presented in Table 1 and are up to par with Tiger winners score.
- We demonstrate a high correlation (Pearson’s coefficient: 0.86) between the computed TILs score and the ground truth (Fig. 2).
- Raw scores computed by the algorithm are consistently below those provided by pathologists: it seems that through eye-balling, practicians tend to overestimate the surface ratio between lymphocytes and stroma. To compensate for this shift, a corrective coefficient ɑ ≈ 4.6 is applied to obtain the final TILs score.
Errors analysis — Some of the main sources of error are:
- Cases where the stroma and epithelium are intertwined
- When the DCIS mimics the IDC especially when the DCIS is inflamed
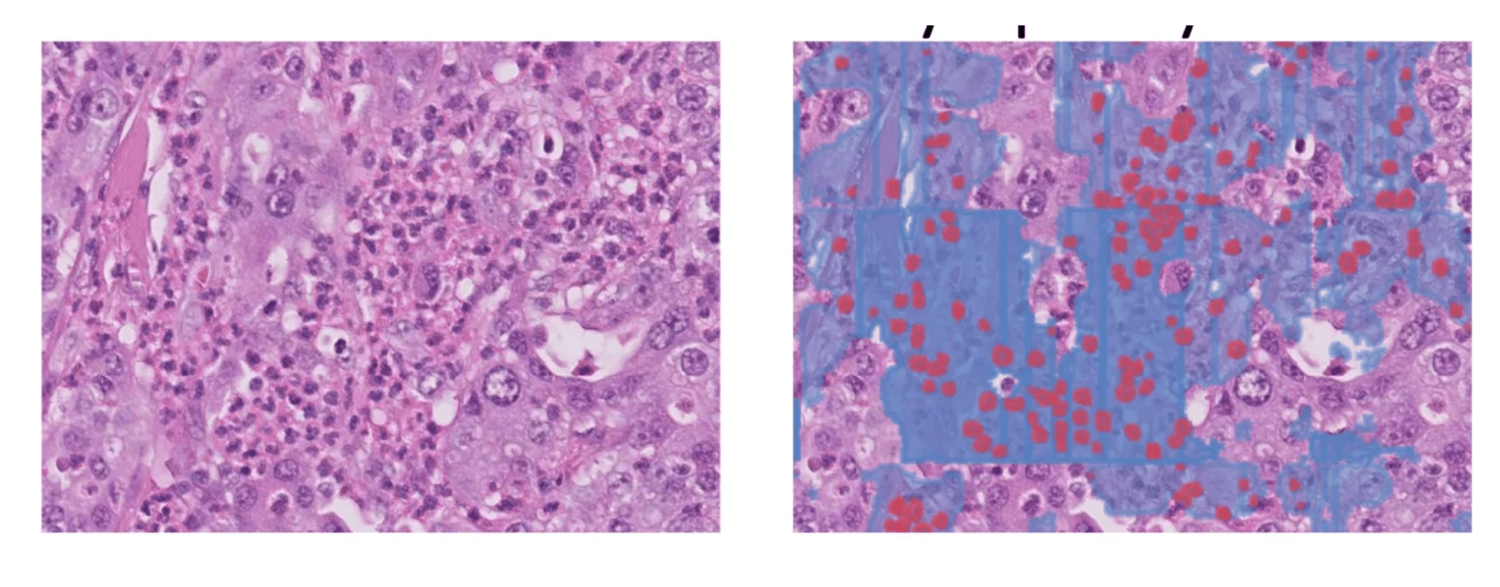
- Granulocytes are often confused with lymphocytes
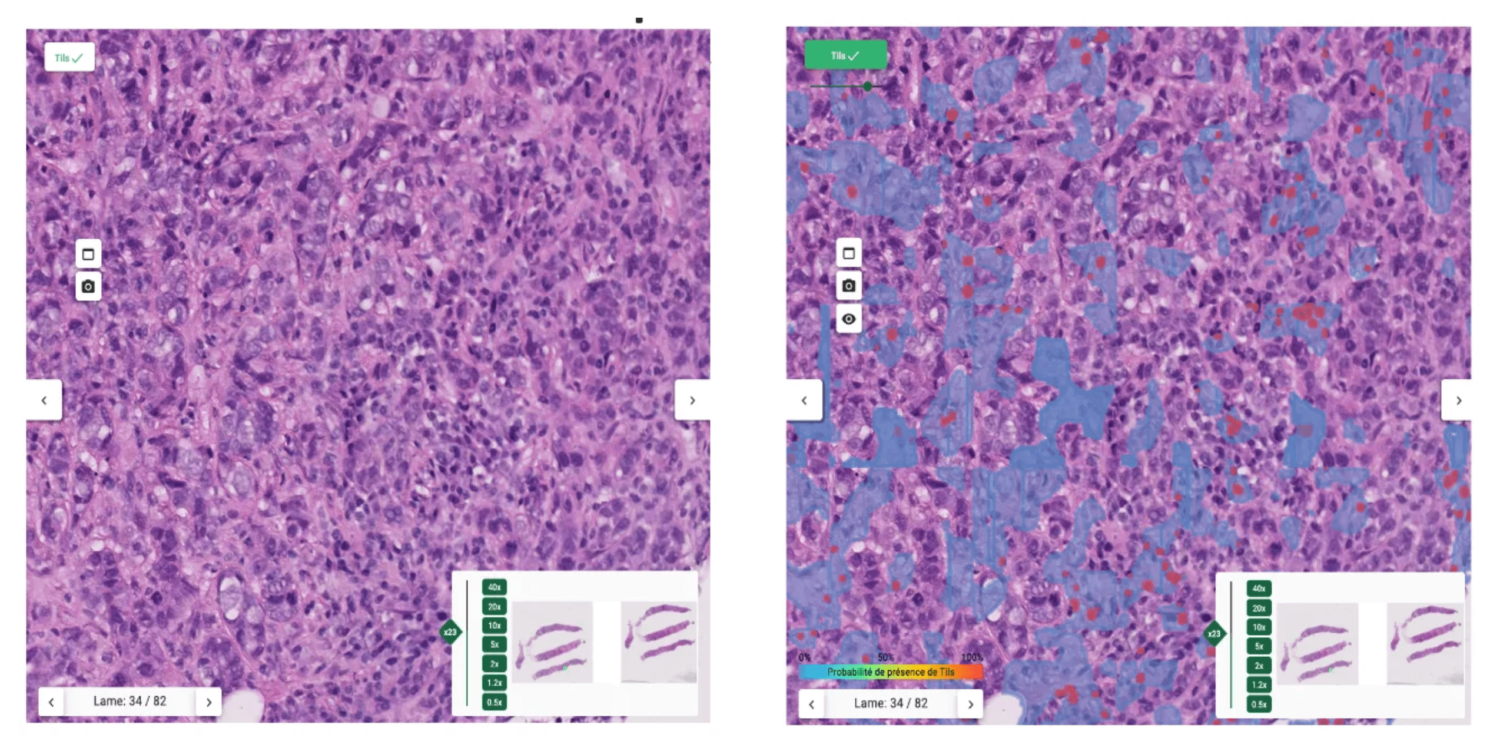
The proposed interface
The heatmap helps pathologists not to focus on hotspots and give score more representative of the true distribution of sTILs density.
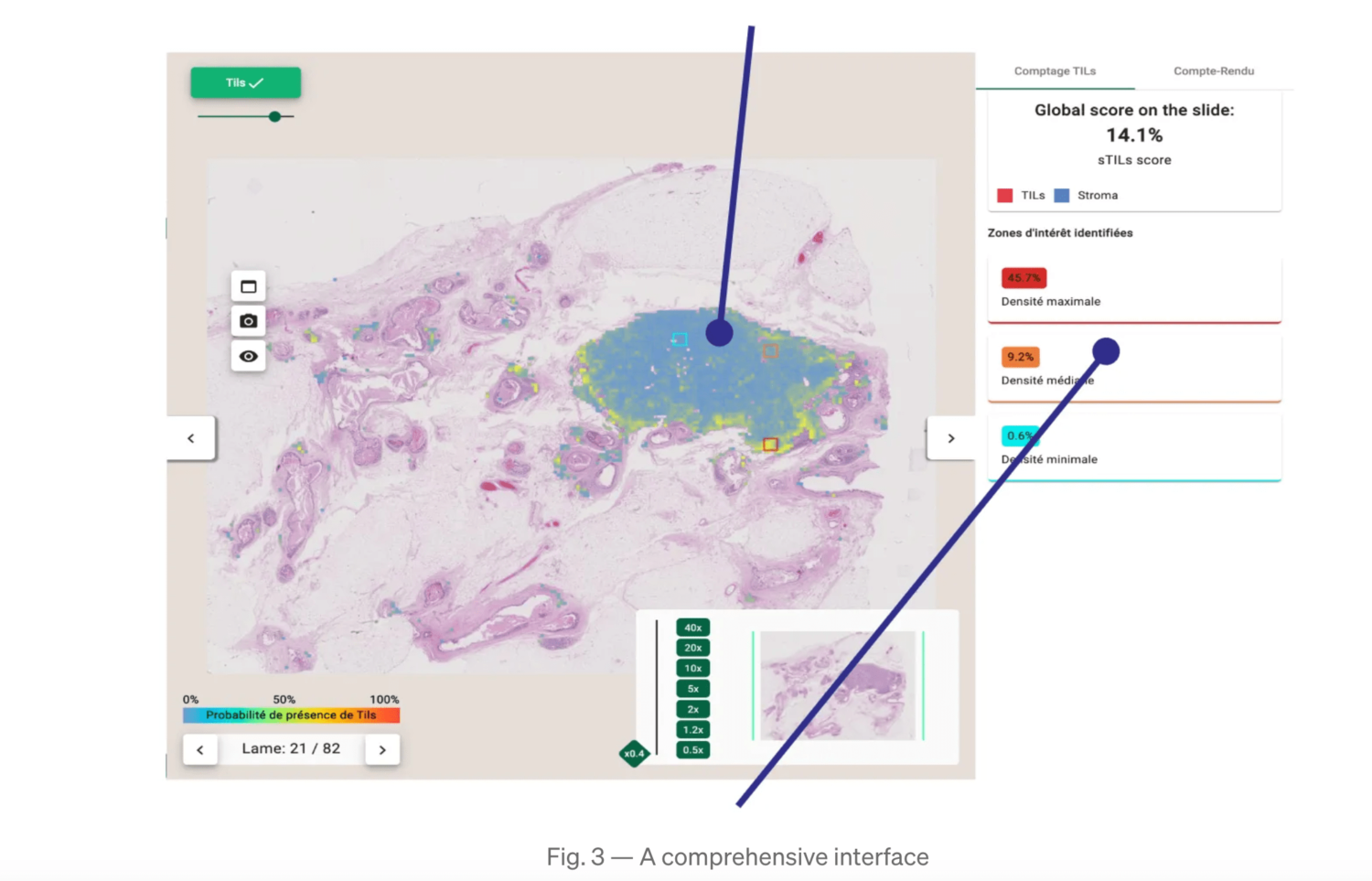
In order to show a variation of TILs density, 3 ROIs are displayed (the highest, lowest and median density ROIs) with their local sTILs score. Within these ROIs, segmentation maps are displayed for explainability.
Conclusions
The automated TILs scoring tool proposed here is highly accurate.
We propose a tool for Computer-Aided TILs assessment, using TILs heatmap and ROI proposal:
- helps preventing biases
- characteristic regions proposal
- explainability
Some difficult cases are still to be tackled (DCIS-like IDC, granulocytes vs lymphocytes, intertwined stroma and epithelium).
You can discover the complete Cleo Breast tool here.
***
[1] Amgad, M., Stovgaard, E.S., Balslev, E. et al. Report on computational assessment of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes from the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group. npj Breast Cancer 6, 16 (2020).
[2] Kos, Z., Roblin, E., Kim, R.S. et al. Pitfalls in assessing stromal tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (sTILs) in breast cancer. npj Breast Cancer 6, 17 (2020).
[3] Tiger challenge, https://tiger.grand-challenge.org/home/, online resource.
[4] Nerrienet, N., Peyret, R., Sockeel, M., & Sockeel, S. (2023). Standardized CycleGAN training for unsupervised stain adaptation in invasive carcinoma classification for breast histopathology. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.13128.
[5] https://rumc-gcorg-p-public.s3.amazonaws.com/evaluation-supplementary/636/ffae22c1-f205-4913-8490-ca878626a7ea/Tiger_Method_writing.pdf, online resource

