POSTER - ECP 2024
End-to-end Pipeline for Automatic Grading of Ki67 in Breast Cancer
By : Nicolas Nerrienet (Primaa), Clara Simmat (Primaa), Rémy Peyret (Primaa), Samuel Touioui (CHU Nancy), Marie Sockeel (Primaa), Bastien Jean Jacques (CHU Caen), Elise Sauvain (CHU Reims), Stéphane Sockeel (Primaa), Elisabeth Lanteri (Medipath).
Introduction
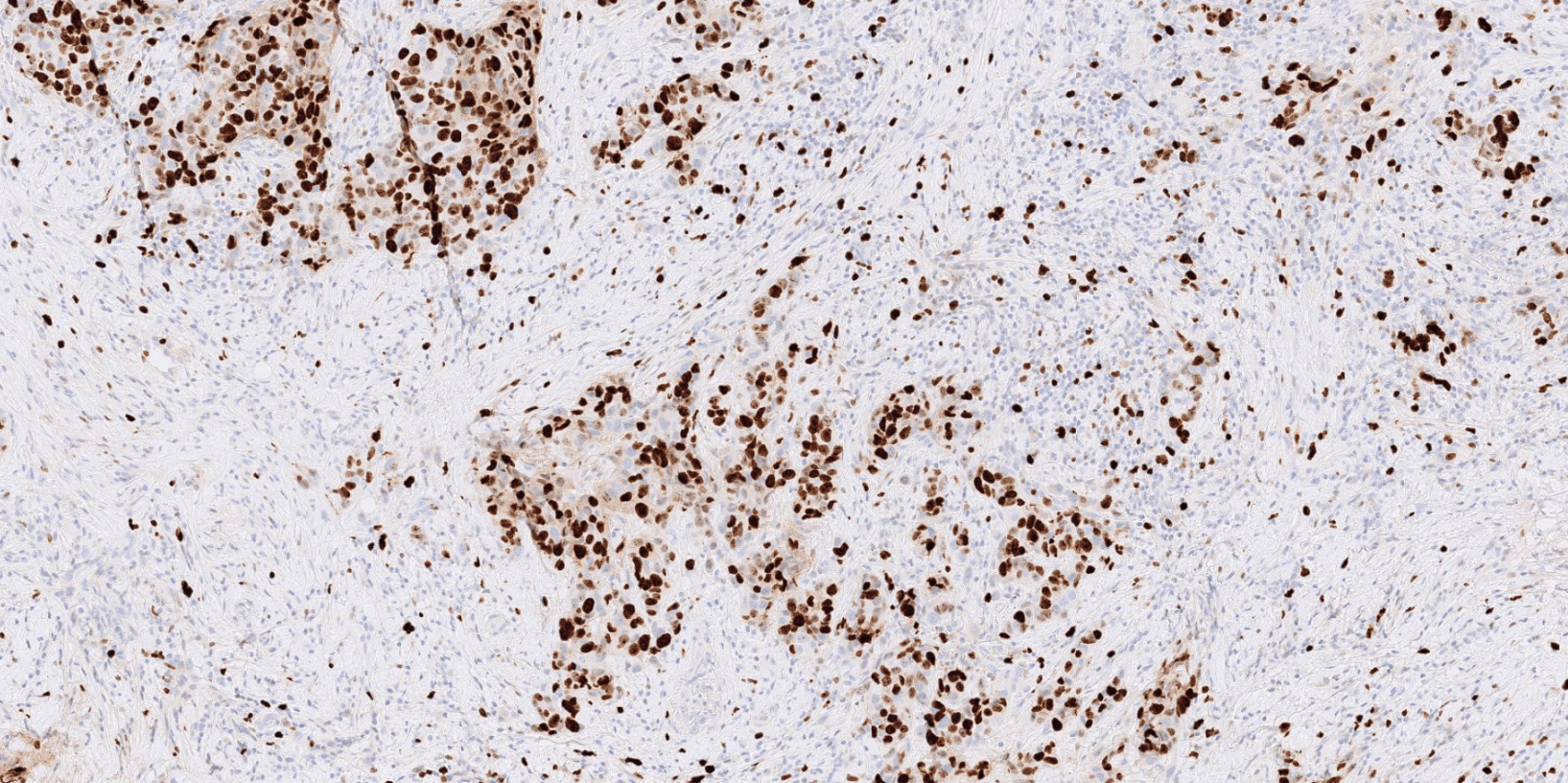
Immuno-histochemistry (IHC) is a staining process that highlights biomarkers like Ki67, important for assessing prognosis and guiding therapeutic decisions. Grading Ki67 in IHC-stained slides involves:
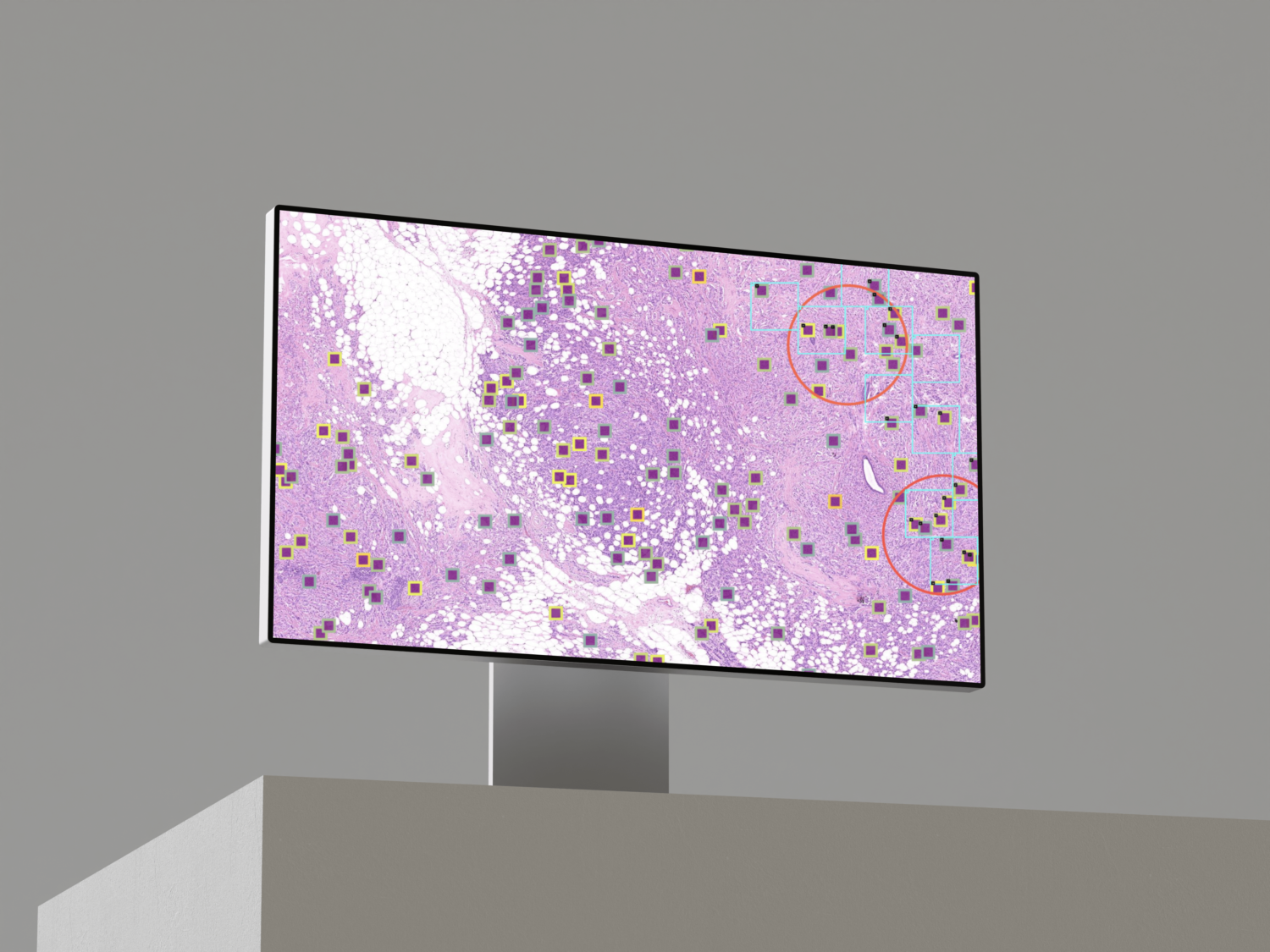
- Identifying invasive carcinoma (IC) regions in hematoxylin-eosin (HE)
- Locating them in associated IHC-stained slides evaluating the presence of target antigens for each nuclei in IC regions by calculating the ratio r between the number of positive nuclei and the total number of nuclei.
- Categories are defined as follow: low if r<=5%, medium if 5%<r<30% and high if r>=30%.
This process is tedious and time consuming. It has also proven to hold high inter-observer variability. Artificial intelligence (AI)-based systems could efficiently assist pathologists in a more accurate clinical diagnosis.
Material & Methods
Datasets & Training
IC detection. Fine-tuning a HE EfficientNet on KI67.

Inference pipeline
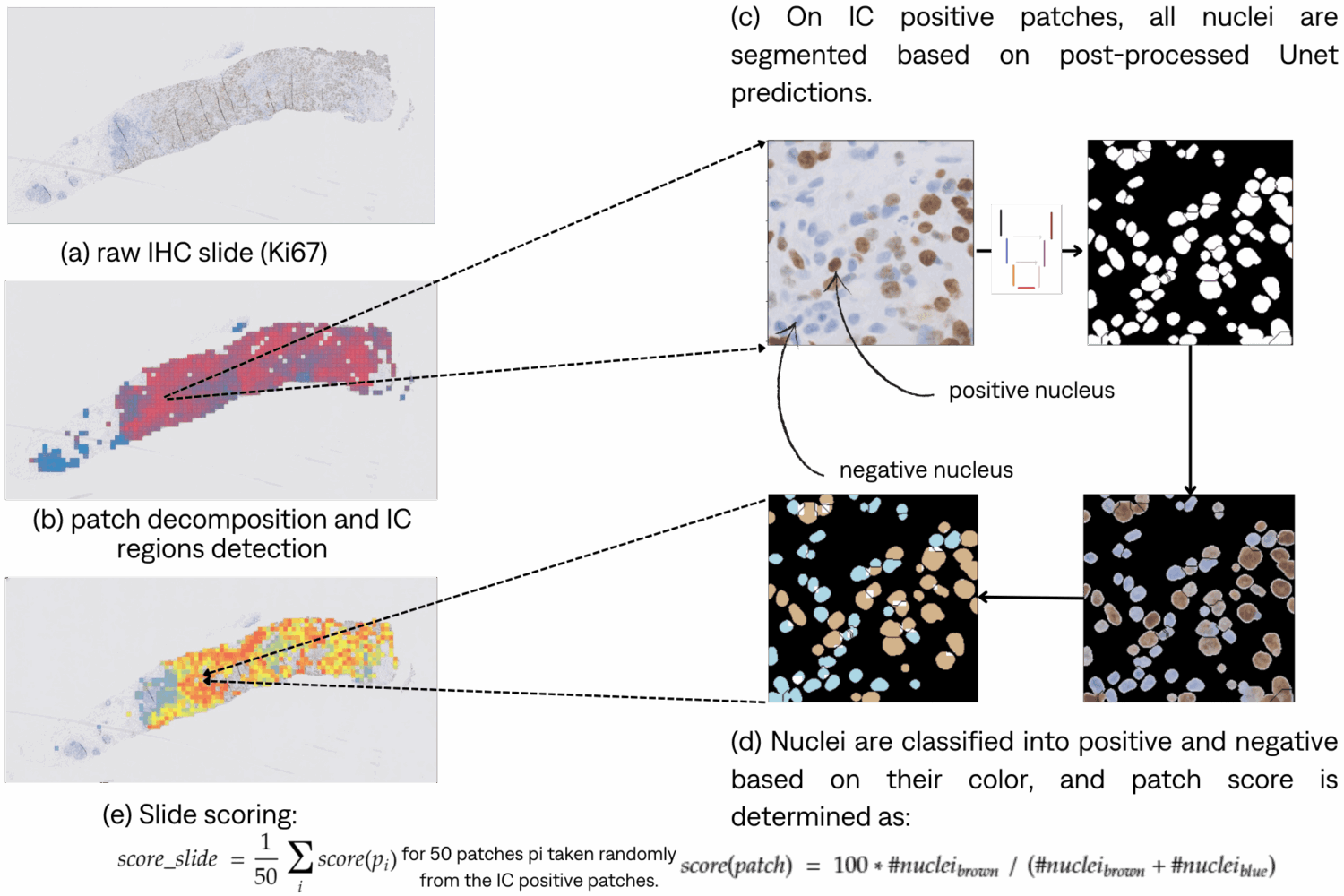
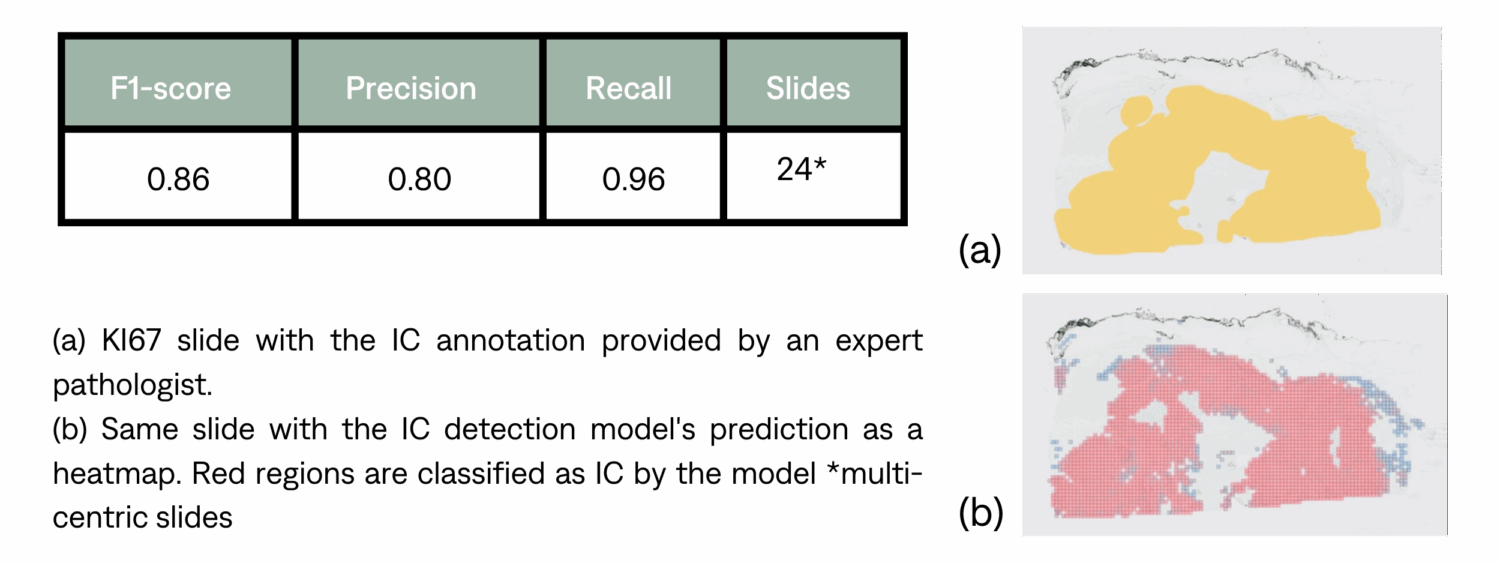
IC detection
Ki67 score and class determination
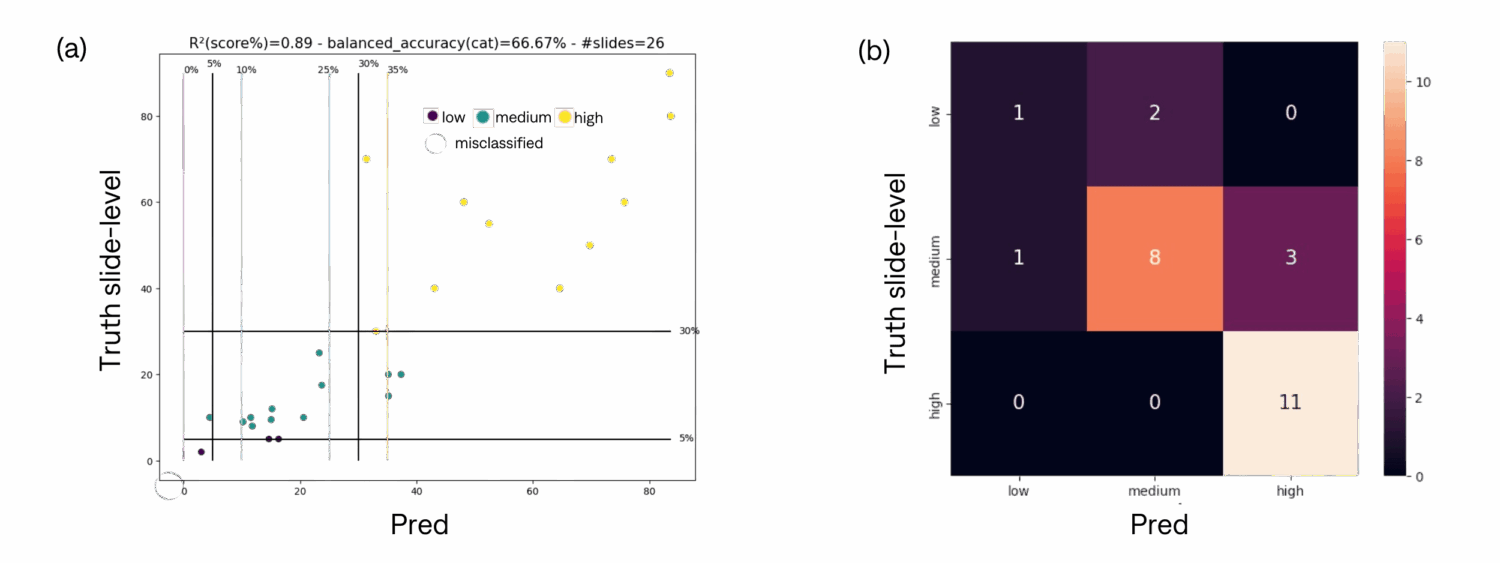
We tested the end-to-end pipeline presented in the previous section for 26 slides from 2 different centers. To measure the quality of scoring, we assessed two metrics: r², the correlation coefficient between the ratio assigned by the pathologist and the ratio provided by the algorithm, and the balanced accuracy across the corresponding categories. Here are (a) the scatter plot of predictions against ground truth with categories thresholds (with a 5% error margin) and (b) the corresponding confusion matrix.
Discussion
We observe a strong correlation (R²=0.89) between the predicted and ground truth Ki67 slides score. Out of 26 slides, 5 were misclassified. However, 3 of these misclassified slides fall within a 5% margin of error, indicating their proximity to the true values. As a limitation, the current pipeline does not differentiate between carcinoma nuclei and non-carcinoma nuclei, which can result in inaccurate scores since the score should only be calculated based on carcinoma nuclei.
Conclusion
In this work, we developed a complete end-to-end pipeline capable of *detecting IC regions directly on IHC stained slidesand *scoring KI67 using those regions. To the best of our knowledge, this end-to-end tool is the first of its kind as existing solutions ask pathologists to select an IC region for the score to be computed in. Our results indicate that the proposed pipeline has a great potential to assist pathologists with their daily routine.

